Investing in the stock market requires a good understanding of different analytical tools to make informed decisions. Two of the most common approaches to analyzing stocks are Fundamental Analysis and Technical Analysis. Each of these approaches provides unique insights into how stocks behave, but they differ significantly in their methodologies. For those interested in developing these skills, enrolling in a program like an advanced technical analysis course or exploring stock market courses in Ahmedabad can provide a comprehensive understanding of these techniques.
We will delve into the core concepts of both fundamental and technical analysis, their differences, and how investors use them to make better decisions in the stock market.
What is Fundamental Analysis?
Fundamental analysis is an approach used to evaluate a company’s intrinsic value by examining various economic, financial, and qualitative factors. This method looks at the fundamentals of the business, including financial statements, industry conditions, management quality, and macroeconomic indicators.
Key Components of Fundamental Analysis:
- Financial Statements: Investors look at a company’s financial health through its balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement. These documents help to determine profitability, revenue growth, and overall financial stability.
- Earnings and Revenue: The revenue and earnings of a company are key indicators of its financial health. Analysts look at the past performance and future projections to assess whether a stock is under- or over-valued.
- P/E Ratio: The Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio is a commonly used metric that helps compare the price of a company’s stock to its earnings. A lower P/E ratio might suggest a stock is undervalued, while a higher ratio could indicate overvaluation.
- Growth Potential: Companies with solid growth potential often have a competitive edge in the market. Analysts evaluate factors like market share, competitive advantages, and business expansion to determine growth prospects.
- Macroeconomic Factors: The overall economic environment, including inflation rates, interest rates, and political stability, plays a significant role in shaping company performance and stock prices.
Fundamental analysts believe that the stock market will eventually reflect the true value of a stock based on its fundamentals, even if it is mispriced in the short term. Therefore, long-term investors often use fundamental analysis to identify opportunities for value investing.
What is Technical Analysis?
Technical analysis focuses on predicting future stock price movements based on historical price patterns and trading volumes. Rather than evaluating the intrinsic value of a stock, technical analysts study price charts, patterns, and various indicators to forecast trends.
Key Components of Technical Analysis:
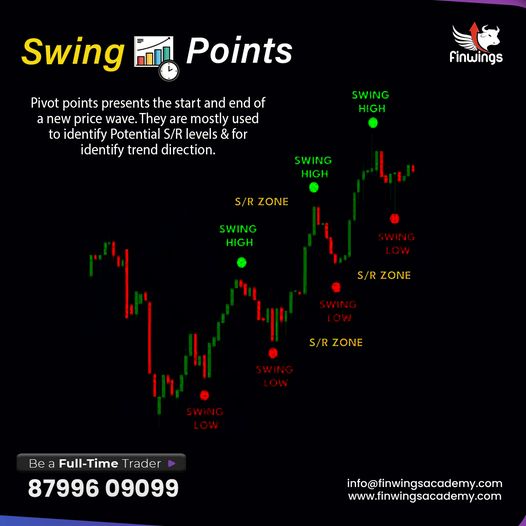
- Price Charts: The most fundamental tool for technical analysis is the price chart. By studying past price movements, analysts attempt to predict future price directions.
- Moving Averages: Moving averages help smooth out price data to form a trend-following indicator. Commonly used moving averages include the 50-day and 200-day averages, which can help identify support and resistance levels.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): RSI is a momentum indicator that measures the speed and change of price movements. It helps to identify overbought or oversold conditions in a stock, signaling potential reversals.
- Volume Analysis: Trading volume helps to confirm trends. If the stock price is increasing on higher volume, it’s considered a stronger trend. Conversely, decreasing volume during a price increase may indicate weakness.
- Support and Resistance Levels: These levels indicate where a stock’s price tends to stop and reverse its direction. Support levels are where a price decline halts, while resistance levels are where a price increase stalls.
Technical analysis is often favored by short-term traders who focus on timing their trades based on price movements. Unlike fundamental analysis, which may take months or years to show results, technical analysis can provide quicker, actionable insights into short-term price movements.
Differences Between Fundamental and Technical Analysis
Both methods have their own set of advantages and limitations, and they cater to different types of investors.
- Time Horizon:
- Fundamental analysis is more suited for long-term investing since it focuses on a company’s future performance based on its financials and economic factors.
- Technical analysis, on the other hand, is used by short-term traders to predict quick price movements.
- Focus:
- Fundamental analysis looks at the “why” behind a stock’s price movement, examining the company’s intrinsic value.
- Technical analysis, however, focuses solely on the price movements and patterns, with no concern for the underlying fundamentals of the business.
- Data Utilization:
- Fundamental analysis requires detailed data like financial reports, economic indicators, and qualitative assessments of management and the industry.
- Technical analysis relies on price charts, volume data, and mathematical indicators to make decisions.
- Objective:
- Fundamental analysis seeks to find the true value of a stock and determines whether it’s undervalued or overvalued.
- Technical analysis aims to identify trends and patterns to time market entries and exits effectively.
Which One Should You Use?
The choice between fundamental and technical analysis largely depends on your investment goals. If you’re a long-term investor looking to build a portfolio based on strong companies with growth potential, fundamental analysis might be your go-to strategy. However, if you’re a short-term trader interested in capitalizing on price fluctuations, technical analysis will likely be more useful.
Interestingly, many professional investors use a combination of both methods. For example, you might use fundamental analysis to find fundamentally strong stocks and then use technical analysis to determine the best time to buy or sell them.
Conclusion
Both fundamental and technical analysis are essential tools for investors, each offering different insights into stock price movements. While fundamental analysis focuses on evaluating a company’s value based on its financial health and broader economic factors, technical analysis focuses on price movements and trends. By taking advanced technical analysis courses or enrolling in stock market courses in Ahmedabad, investors can gain a deeper understanding of both methods and become more skilled in making informed investment decisions.
:strip_icc():format(webp)/kly-media-production/medias/3484158/original/092869100_1623829797-Bank_Dunia_2.jpg)
:strip_icc():format(webp)/kly-media-production/medias/4744027/original/052406200_1708001910-GUS_IQDAM_GIBRAN_3.JPG)
:strip_icc():format(webp)/kly-media-production/medias/4648806/original/068385700_1699975170-20231114-Pengundian_No_Urut-FAI_1.jpg)
:strip_icc():format(webp)/kly-media-production/medias/4844263/original/024291900_1716810482-Infografis_SQ_Program_Makan_Siang_Gratis_Prabowo-Gibran_Diubah_Jadi_Makan_Bergizi_Gratis.jpg)